JAVA TUTORIAL
Java Intro Java Features Java vs C++ Java Simple Program Java Applet vs Application JVM,JDK or JRE Java Keywords Java Variables Java Literals Java Separators Java Datatypes Java Operators Java Statements Java Array Java StringCONTROL STATEMENTS
Java If-else Java While Loop Java Do-While Loop Java For Loop Java For-each Loop Java Switch Java Break/ContinueJAVA METHODS
Java Method Java Overloading Java OverridingJAVA CLASSES
Java OOPs Java Classes/Objects Java Inheritance Java Polymorphism Java Encapsulation Java Abstraction Java Modifiers Java Constructors Java Interface Java static keyword Java this keywordData Types is Java
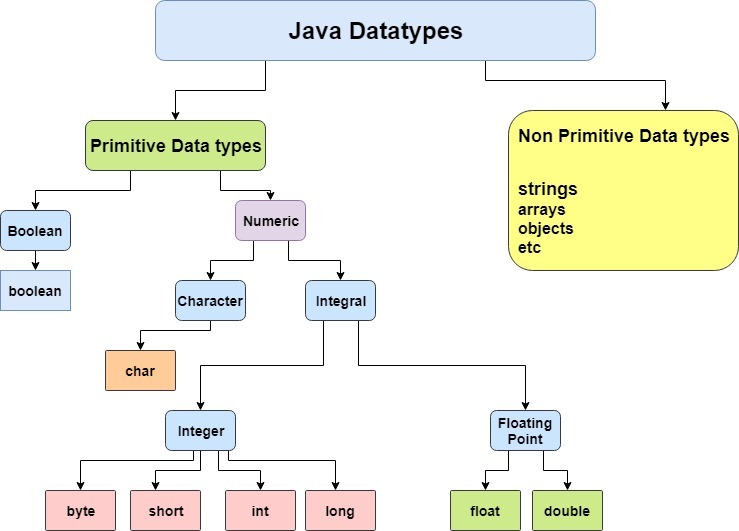
It specify the different sizes and type of values that can be stored in the variable. There are two types of data types in Java Language:
1. Primitive data types: The primitive data types include byte, short, int, long, boolean, char, float and double.
2. Non-primitive data types: The non-primitive data types include Classes, Arrays, Interface etc.
Primitive Data Types
In Java language, primitive data type specifies the size and type of variable values and also have no special capabilities.
There are eight primitive data types available in Java language.They are:
1. boolean
2. char
3. byte
4. short
5. int
6. long
7. float
8. double
boolean:
A boolean data type is declared with the boolean keyword and can only take the values true or false. This data type is used for simple flags that track true/false conditions.The Boolean data type specifies one bit of information, but its "size" can't be defined precisely.
Syntax:
boolean booleanVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
boolean b = true;
if (b == true)
System.out.println("Hii.. Boolean");
}
}Output:
Hii.. Boolean
char:
The char data type is a single 16-bit Unicode character. The character must be surrounded by single quotes, like 'R' or 'j':
Syntax:
char charVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
char c = 'R';
System.out.println("Hii.. "+c);
}
}Output:
Hii.. R
byte:
The byte data type is an example of primitive data type. The byte data type is an 8-bit signed two’s complement integer. The byte data type is useful for saving memory in large arrays. Its minimum value is -128 and maximum value is 127. Its default value is 0.
Syntax:
byte byteVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
byte b = 122;
System.out.println(b);
}
}Output:
122
short:
The short data type is a 16-bit signed two's complement integer. Use a short to save memory in large arrays, in situations where the memory savings actually matters. Its minimum value is -32,768 and maximum value is 32,767. Its default value is 0.
Syntax:
short shortVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
short s = 5000;
System.out.println(s);
}
}Output:
5000
int:
The int data type is a 32-bit signed two's complement integer. Its minimum value is - 2,147,483,648and maximum value is 2,147,483,647. Its default value is 0.
Syntax:
int intVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a = 52000;
System.out.println(a);
}
}Output:
52000
long:
The long data type is a 64-bit two's complement integer. Used when int is not large enough to hold the value, it has wider range than int data type, ranging from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. Its minimum value is - 9,223,372,036,854,775,808and maximum value is 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. Its default value is 0.
Syntax:
long longVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
long l = 123456023;
System.out.println(l);
}
}Output:
123456023
float:
The float data type is a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point.Its value range is unlimited. Use a float (instead of double) if you need to save memory in large arrays of floating-point numbers.
Syntax:
float floatVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
float f = 4.73334f;
System.out.println(f);
}
}Output:
4.733343
double:
The double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating-point. For decimal values, this data type is generally the default choice. The double data type also should never be used for precise values, such as currency. Its default value is 0.0d.
Syntax:
double doubleVarName;Example
class CodeTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
double d = 42.2;
System.out.println(d);
}
}Output:
42.2